RMAN backup set, pieces, and datafiles
RMAN backs up the datafiles, control file, archived log files, and server parameter files in a RMAN specific format called a backup piece. In a nutshell, a backup set is a bundle of dbf, ctl and redo file that can restore a database. A set of one or more such backup pieces makes up a backup set. A backup set is created using the BACKUP command.
Useful views for backup query
V$BACKUP_SET displays information about backup sets from the control file. A backup set record is inserted after the backup set is successfully completed. The backup set stamp (SET_STAMP) and count (SET_COUNT) uniquely identify the backup set.
V$BACKUP_PIECE displays information about backup pieces from the control file. Each backup set consists of one or more backup pieces.
V$BACKUP_DATAFILE displays information about control files and datafiles in backup sets from the control file.
V$BACKUP_FILES displays information about all RMAN backups (both image copies and backup sets) and archived logs.This view simulates the LIST BACKUP and LIST COPY RMAN commands. This view requires that the database be set using the DBMS_RCVMAN.SETDATABASE procedure.
Useful SQL statements
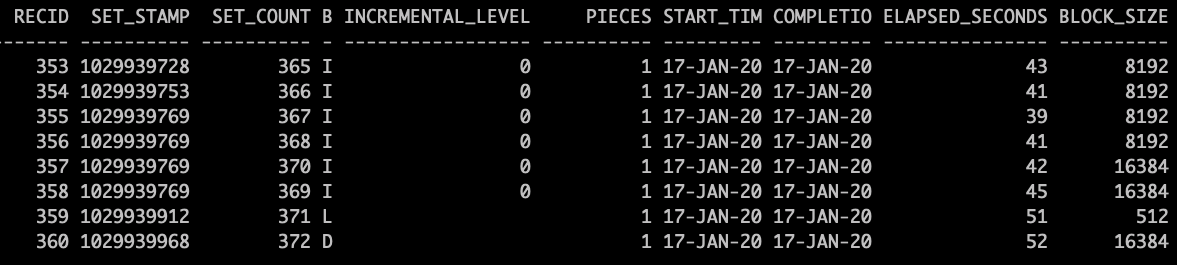
Query backup set information. The very last record(e.g. RECID=360) could be used as the start point for future queries.
SQL> select recid, set_stamp, set_count, backup_type,incremental_level,pieces,start_time,completion_time,elapsed_seconds,block_size from v$backup_set;
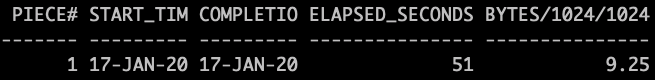
Query backup pieces for certain backup set.
SQL> select piece#,compressed,start_time,completion_time,elapsed_seconds,bytes/1024/1024 from v$backup_piece where set_stamp=1029939968 and set_count=372;
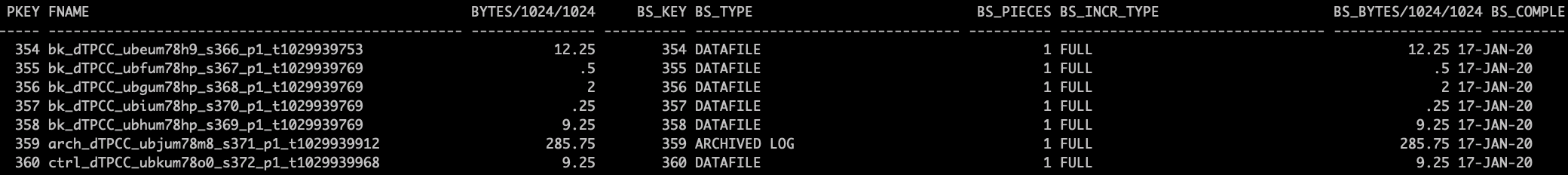
Query backup files for certain backup set.
SQL> select pkey,fname,file_type,bytes/1024/1024,bs_key,bs_type,bs_pieces,bs_incr_type,bs_bytes/1024/1024, bs_completion_time from v$backup_files where FILE_TYPE=’PIECE’order by bs_key;
SQL> select pkey,file_type, fname, bytes/1024/1024,bs_key,bs_type,bs_incr_type,bs_bytes/1024/1024 from v$backup_files where bs_key=360;

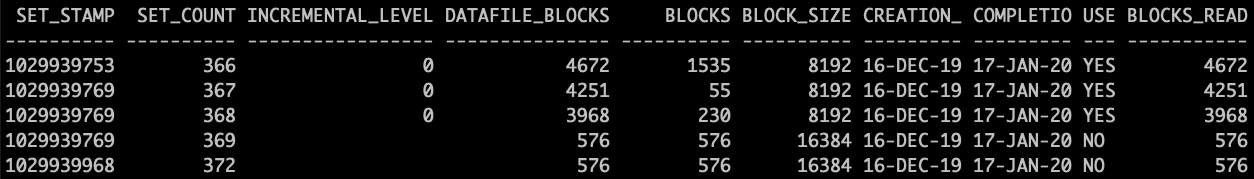
Query total blocks and read blocks for certain backup set.
SQL> select set_stamp,set_count,incremental_level,datafile_blocks,blocks,block_size, CREATION_TIME ,completion_time,used_change_tracking,blocks_read from v$backup_datafile where set_count>365;
Query total blocks and read blocks for certain backup. The following example checks the read and write ratio when BCT is enabled and a full backup is done.
SQL> select sum(BLOCKS_READ*BLOCK_SIZE)/1024/1024/1024 read_GB from v$backup_datafile where USED_CHANGE_TRACKING = ‘YES’;
READ_GB
1195.7244SQL> select sum(BLOCKS*BLOCK_SIZE)/1024/1024/1024 write_GB from v$backup_datafile where USED_CHANGE_TRACKING = ‘YES’;
WRITE_GB898.733315
SQL> select sum(DATAFILE_BLOCKS*BLOCK_SIZE)/1024/1024/1024 datafile_GB from v$backup_datafile where USED_CHANGE_TRACKING = ‘YES’;
DATAFILE_GB
1195.7244SQL> select sum(BLOCKS_READ)/sum(DATAFILE_BLOCKS) from v$backup_datafile where USED_CHANGE_TRACKING = ‘YES’;
SUM(BLOCKS_READ)/SUM(DATAFILE_BLOCKS)
1
SQL> select sum(BLOCKS)/sum(DATAFILE_BLOCKS) from v$backup_datafile where USED_CHANGE_TRACKING = ‘YES’;SUM(BLOCKS)/SUM(DATAFILE_BLOCKS)
.751622457The following example checks the read and write blocks ratio after incremental backup is done which is based on previous full backup. The write blocks ratio can be treated as data change ratio.
$ cat bct_check.sql
set linesize 500;select set_stamp,set_count,incremental_level, used_change_tracking,blocks_read,blocks,datafile_blocks,block_size from v$backup_datafile where set_count>372 order by set_count;
select sum(BLOCKS_READ*BLOCK_SIZE)/1024/1024/1024 read_GB from v$backup_datafile where set_count>372;
select sum(BLOCKS*BLOCK_SIZE)/1024/1024/1024 write_GB from v$backup_datafile where set_count>372;
select sum(DATAFILE_BLOCKS*BLOCK_SIZE)/1024/1024/1024 total_GB from v$backup_datafile where set_count>372;
select sum(BLOCKS_READ)/sum(DATAFILE_BLOCKS) “%READ” from v$backup_datafile where set_count>372;
select sum(BLOCKS)/sum(DATAFILE_BLOCKS) “%WRITE” from v$backup_datafile where set_count>372;
exit
$ sqlplus / as sysdba @bct_check.sql
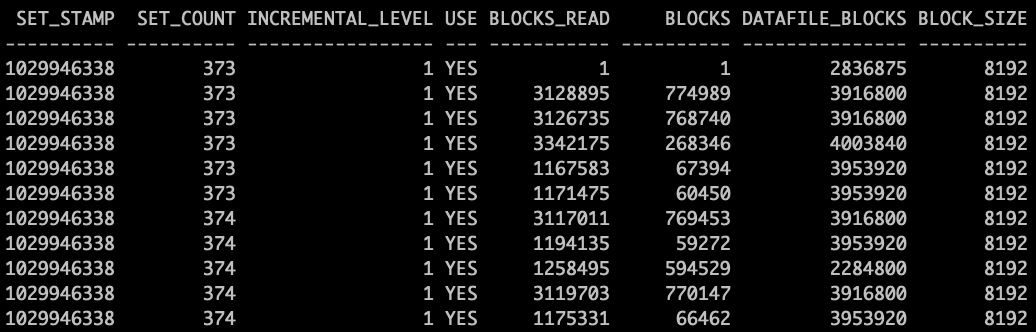
READ_GB
662.855164
WRITE_GB
103.244957
TOTAL_GB
1195.75419
%READ
.554337382
%WRITE
.086336245
The following command also checks total write data during backup.
SQL> select sum(BYTES)/1024/1024/1024 from v$backup_piece where set_count>372;
SUM(BYTES)/1024/1024/1024
130.938721