Level 0 and Level 1 Incremental Backups
Incremental backups can be either level 0 or level 1. A level 0 incremental backup, which is the base for subsequent incremental backups, copies all blocks containing data, backing the datafile up into a backup set just as a full backup would. The only difference between a level 0 incremental backup and a full backup is that a full backup is never included in an incremental strategy.
A level 1 incremental backup can be either of the following types:
- A differential backup, which backs up all blocks changed after the most recent incremental backup at level 1 or 0
- A cumulative backup, which backs up all blocks changed after the most recent incremental backup at level 0
Incremental backups are differential by default.
The size of the backup file depends solely upon the number of blocks modified and the incremental backup level.
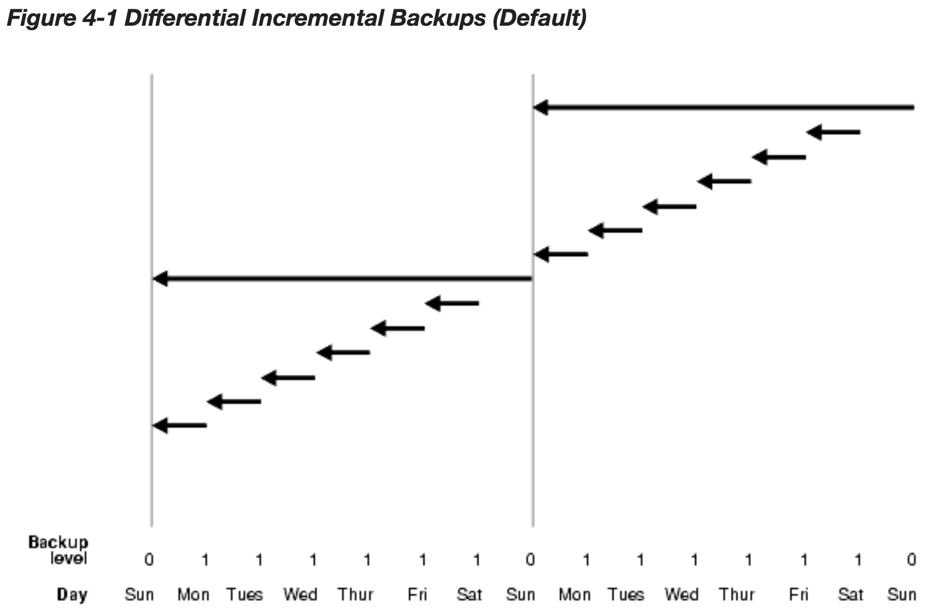
In the example shown above, the following occurs:
- Sunday
An incremental level 0 backup backs up all blocks that have ever been in use in this database.
- Monday - Saturday
On each day from Monday through Saturday, a differential incremental level 1 backup backs up all blocks that have changed since the most recent incremental backup at level 1 or 0. So, the Monday backup copies blocks changed since Sunday level 0 backup, the Tuesday backup copies blocks changed since the Monday level 1 backup, and so forth.
- The cycle is repeated for the next week.
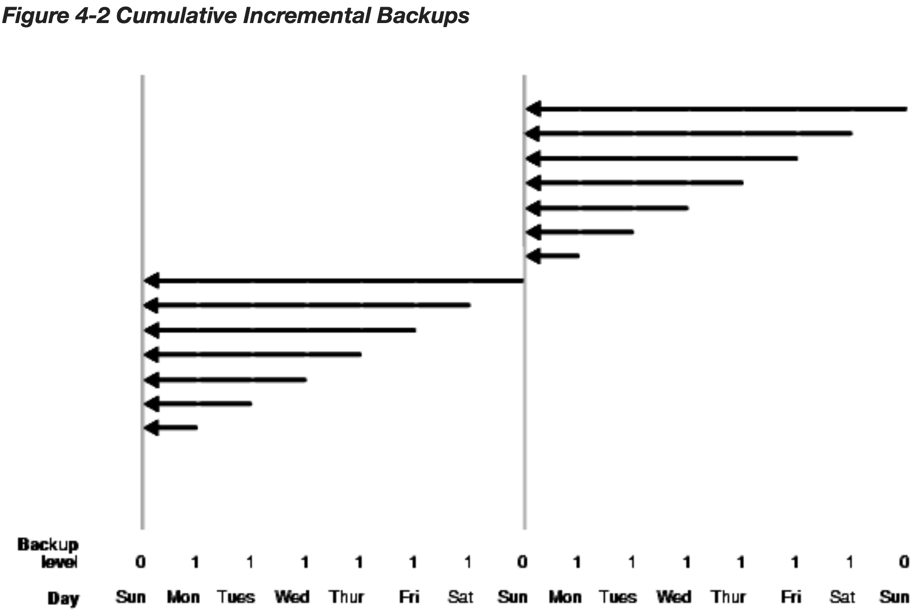
In the example shown above, the following occurs:
- Sunday
An incremental level 0 backup backs up all blocks that have ever been in use in this database.
- Monday - Saturday
A cumulative incremental level 1 backup copies all blocks changed since the most recent level 0 backup. Because the most recent level 0 backup was created on Sunday, the level 1 backup on each day Monday through Saturday backs up all blocks changed since the Sunday backup.
- The cycle is repeated for the next week.
Incremental Backup Algorithm
Each data block in a datafile contains a system change number (SCN), which is the SCN at which the most recent change was made to the block. During an incremental backup, RMAN reads the SCN of each data block in the input file and compares it to the checkpoint SCN of the parent incremental backup. If the SCN in the input data block is greater than or equal to the checkpoint SCN of the parent, then RMAN copies the block.
Note that if you enable the block change tracking feature, RMAN can refer to the change tracking file to identify changed blocks in datafiles without scanning the full contents of the datafile. Once enabled, block change tracking does not alter how you take or use incremental backups, other than offering increased performance.